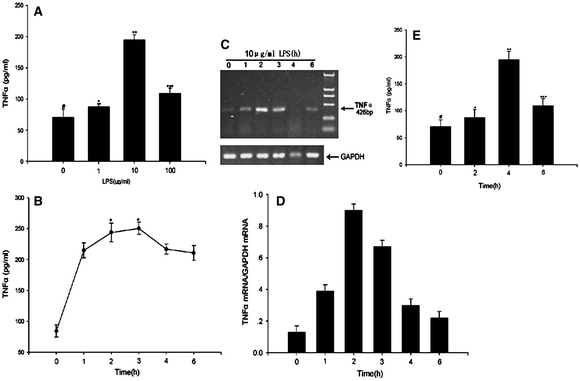
TLR4-mediated IRAK1 activation induces TNF-α expression via JNK-dependent NF-κB activation in human bronchial epithelial cells - Sae Hoon Park, Hye-Jin Choi, So Young Lee, Joong-Soo Han, 2015

LPS-induced TNF-α factor (LITAF)-deficient mice express reduced LPS-induced cytokine: Evidence for LITAF-dependent LPS signaling pathways | PNAS
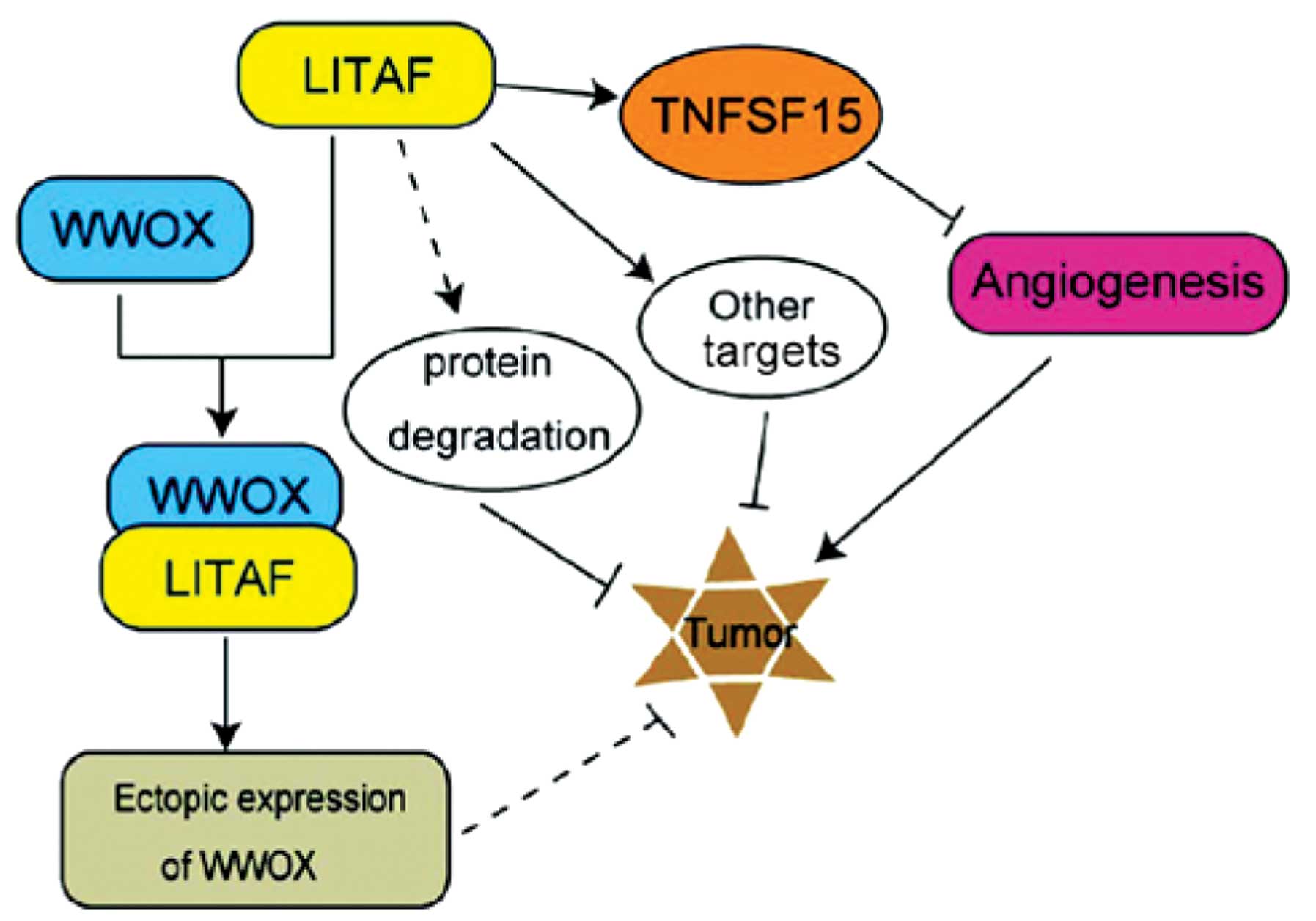
Lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-α factor enhances inflammation and is associated with cancer (Review)

β-Ionone attenuates LPS-induced pro-inflammatory mediators such as NO, PGE2 and TNF-α in BV2 microglial cells via suppression of the NF-κB and MAPK pathway - ScienceDirect
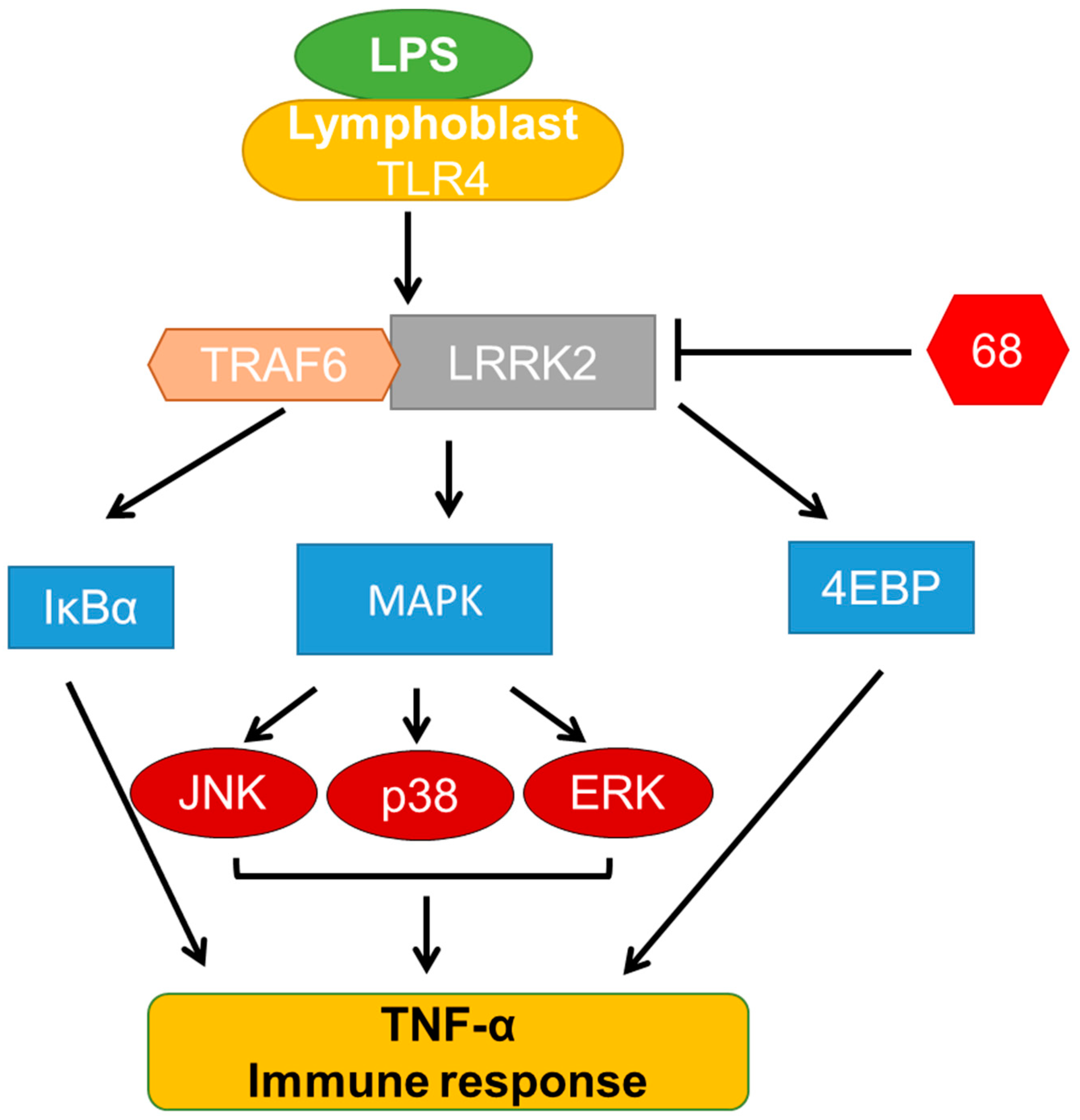
Cells | Free Full-Text | A LRRK2 GTP Binding Inhibitor, 68, Reduces LPS-Induced Signaling Events and TNF-α Release in Human Lymphoblasts
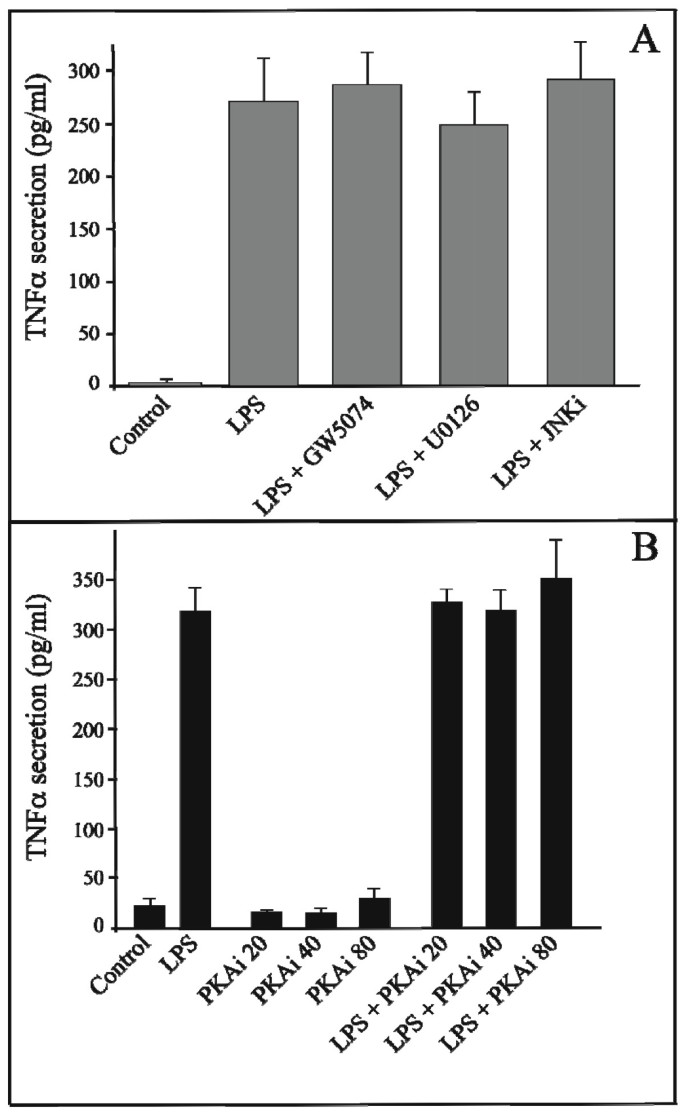
Signaling pathways involved in LPS induced TNFalpha production in human adipocytes | Journal of Inflammation | Full Text

Suppression of LPS-Induced TNF-α Production in Macrophages by cAMP Is Mediated by PKA-AKAP95-p105 | Science Signaling

Impaired Tumor-Necrosis-Factor-α-driven Dendritic Cell Activation Limits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Protection from Allergic Inflammation in Infants - ScienceDirect
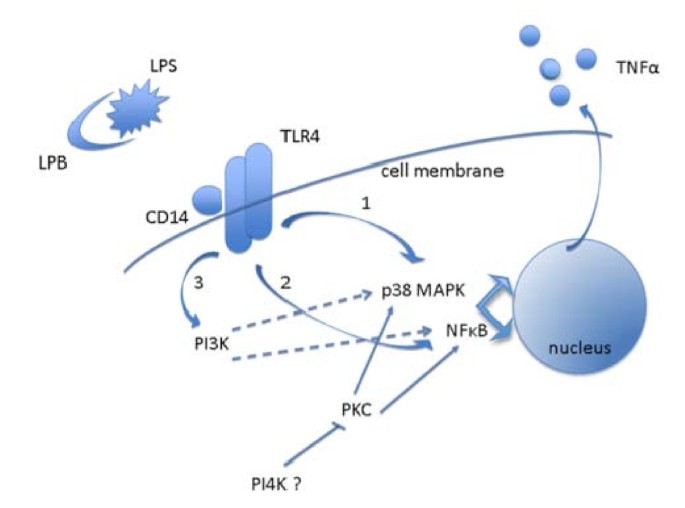
Signaling pathways involved in LPS induced TNFalpha production in human adipocytes | Journal of Inflammation | Full Text

SciELO - Brasil - Increased production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in whole blood cultures from children with primary malnutrition Increased production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in whole blood cultures from children with
![PDF] Atorvastatin Attenuates TNF-alpha Production via Heme Oxygenase-1 Pathway in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophages. | Semantic Scholar PDF] Atorvastatin Attenuates TNF-alpha Production via Heme Oxygenase-1 Pathway in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophages. | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/2bfdb9c666ee18b3a15c85907a882eaa486a5676/4-Figure1-1.png)
PDF] Atorvastatin Attenuates TNF-alpha Production via Heme Oxygenase-1 Pathway in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophages. | Semantic Scholar
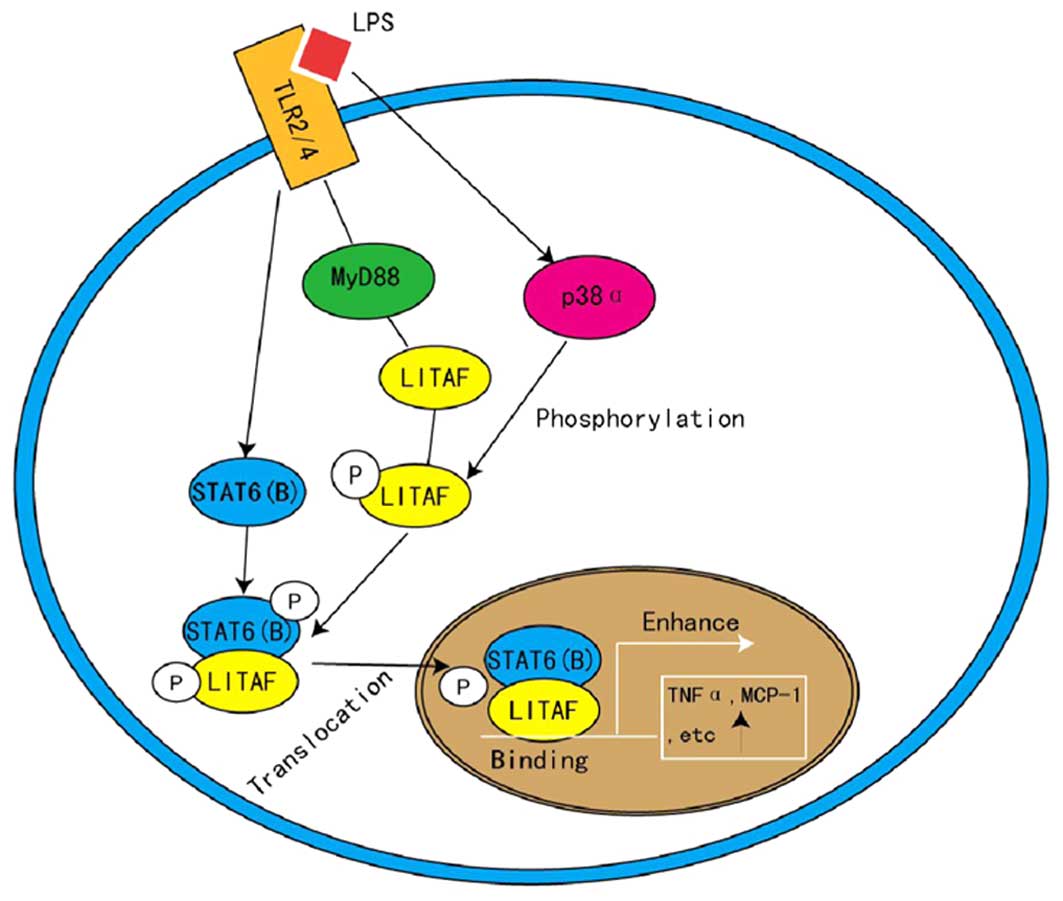
Lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-α factor enhances inflammation and is associated with cancer (Review)

LPS induces the interaction of a transcription factor, LPS-induced TNF-α factor, and STAT6(B) with effects on multiple cytokines | PNAS

Inhibition of LPS-Induced TNF-{Alpha} and NO Production in Mouse Macrophage and Inflammatory Response in Rat Animal Models by a Novel Ayurvedic Formulation, BV-9238 - Global Medical Discovery

Suppression of LPS-Induced TNF-α Production in Macrophages by cAMP Is Mediated by PKA-AKAP95-p105 | Science Signaling
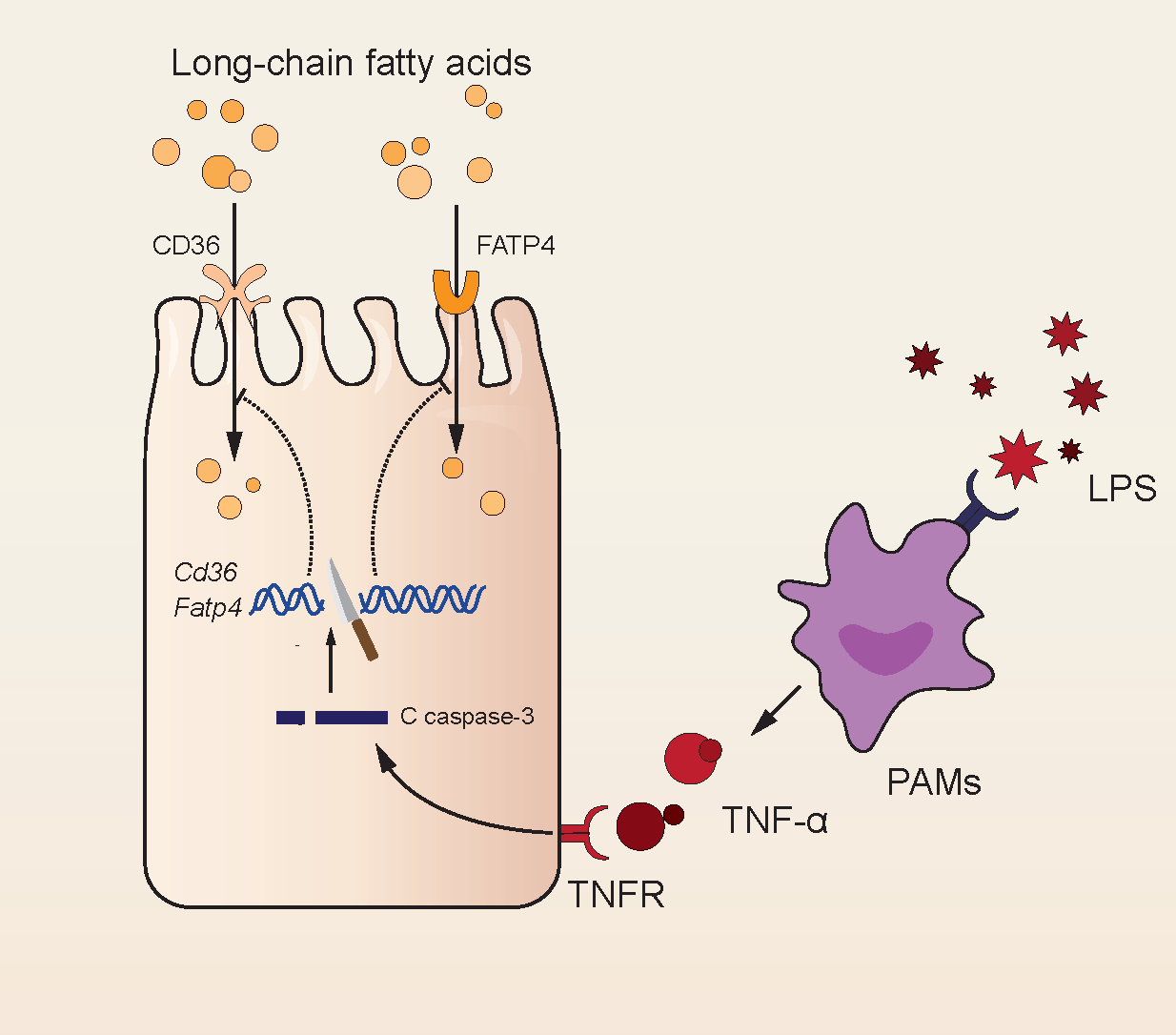
Cells | Free Full-Text | LPS Inhibits Fatty Acid Absorption in Enterocytes through TNF-α Secreted by Macrophages